Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
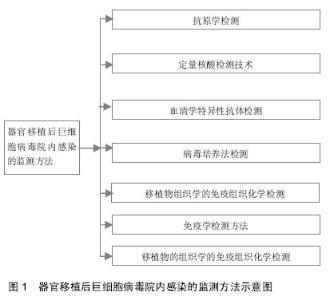
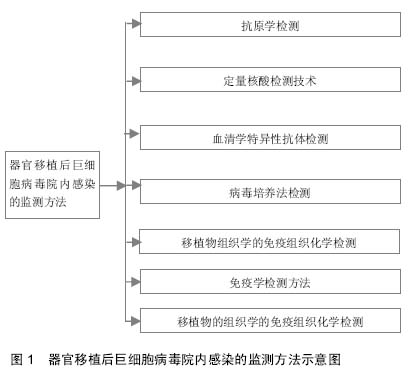
Cytomegalovirus nosocomial infection following organ transplantation: detection and monitoring
Zhang Li-ping, Bai Jian
- Department of Hospital Infection Management, Liaoning Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, Liaoning Province, China
-
Online:2015-05-14Published:2015-05-14 -
Contact:Bai Jian, Department of Hospital Infection Management, Liaoning Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zhang Li-ping, Nurse in charge, Department of Hospital Infection Management, Liaoning Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81170692
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Li-ping, Bai Jian. Cytomegalovirus nosocomial infection following organ transplantation: detection and monitoring [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.20.027 .
share this article
| [1] Craig JM, Macauley JC, Weller TH, et al. Isolation of intranuclear inclusion producing agents from infants with illnesses resembling cytomegalic inclusion disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957:94(1):4-12. [2] Ariza-Heredia EJ, Nesher L, Chemaly RF. Cytomegalovirus diseases after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a mini-review. Cancer Lett. 2014;342(1):1-8. [3] Minton K. Viral immunity: How CMV bypasses immune memory. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(5):288. [4] Bate SL, Dollard SC, Cannon MJ. Cytomegalovirus seroprevalence in the United States: the national health and nutrition examination surveys 1988–2004. Clin Infect. Dis. 2010;50(11):1439-1447. [5] 黄云帆,陈虹,王旭,等.肝移植后巨细胞病毒感染:对排斥反应与移植物的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(27):443-4428. [6] Boeckh M. Complications, Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of CMV Infections: Current and Future. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011; 305-309. [7] Green ML, Leisenring W, Stachel D, et al. Efficacy of a viral load-based, risk-adapted, preemptive treatment strategy for prevention of cytomegalovirus disease after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2012;18(11): 1687-1699. [8] Lisboa LF, Asberg A, Kumar D, et al. The clinical utility of whole blood versus plasma cytomegalovirus viral load assays for monitoring therapeutic response. Transplantation. 2011; 91(2):231-236. [9] Plosa EJ, Esbenshade JC, Fuller MP, et al. Cytomegalovirus Infection. Pediatr Rev. 2012,33(4):156-163. [10] 杨菁,王东.人巨细胞病毒被膜磷蛋白pp65的检测及其在肾移植受者CMV病诊断中的临床应用[J].南方医科大学学报, 2008, 28(2): 263-265. [11] Martin JM, Danziger-Isakov LA. Danziger-Isakov2 Cytomegalovirus risk, prevention, and management in pediatric solid organ transplantation. Pediatr Transpl. 2011; 15(3):229-236. [12] Roman A, Manito N, Campistol JM, et al. The impact of the prevention strategies on the indirect effects of CMV infection in solid organ transplant recipients. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2014;28:84-89. [13] 何小舟,许贤林,叶青,等.肾移植后RT-PCR动态检测巨细胞病毒尿的临床意义[J].苏州大学学报(医学版),2007,7(4):591-594. [14] Hanfler J, Kreuzer KA, Laurisch K, et al. Quantitation of cytomegalovirus (hCMV) DNA and beta-actin DNA by duplex realtime fluorescence PCR in solid organ (liver)transplant recipients. Med Microbiol Inununol. 2003;192(4):197-204. [15] 周文强,石炳毅,蔡明,等.肾移植后受者人巨细胞病毒巢式PCR检测[J].中国实验诊断学杂志,2007,11(5):628-629. [16] Stoeher M, Berg J. Normailized quantification of human cytomegalovious DNA by competitive real-time PCR on the Light Cyrcler instrument. J Clin Microbilol. 2002;40(12): 4547-4553. [17] Mewara A, Mishra B, Ratho RK, et al. Comparison of PCRs for IE-1 and gB genes with ELISA of IgM antibodies for diagnosis of human cytomegalovirus disease. Acta Virol. 2010;54(4):315-316. [18] Ahmadinejad Z, Ardalan FA, Razzaqi M, et al. QuantiFERON-TB Gold in Tube test for diagnosis of latent tuberculosis (TB) in solid organ transplant candidates: a single-center study in an area endemic for TB. Transpl Infect Dis. 2013;15(1):90-95. [19] Longworth SA, Vinnard C, Lee I, et al. Risk factors for nontuberculous mycobacterial infections in solid organ transplant recipients: a case-control study. Transpl Infect Dis. 2014;16:76-83. [20] Giulieri S, Manuel O. QuantiFERON(R)-CMV assay for the assessment of cytomegalovirus cell-mediated immunity. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2011;11(1):17-25. [21] Wiita AP, Roubinian N, Khan Y, et al. Cytomegalovirus disease and infection in lung transplant recipients in the setting of planned indefinite valganciclovir prophylaxis. Transpl Infect Dis. 2012;14(3):248-258. [22] Ren Y, Ding Q, Zhang X. Ficolins and infectious diseases. Virol Sin. 2014;29(1):25-32. [23] Wadhawan M, Gupta S, Goyal N, et al. Cytomegalovirus infection: its incidence and management in cytomegalovirus-seropositive living related liver transplant recipients: a single-center experience. Liver Transpl. 2012; 18(12):1448-1455. [24] Kotton CN. CMV: prevention, diagnosis and therapy. Am J Transpl. 2013;13(s3):24-40. [25] Hoyo I, Sanclemente G, Cervera C, et al. Opportunistic pulmonary infections in solid organ transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2012;44(9):2673-2675. [26] Blyth E, Clancy L, Simms R, et al. Donor-derived CMVspecific T cells reduce the requirement for CMV-directed pharmacotherapy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2013;121(18):3745-3758. [27] Witzke O, Hauser IA, Bartels M, et al. Valganciclovir prophylaxis versus preemptive therapy in cytomegalovirus- positive renal allograft recipients: 1-year results of a randomized clinical trial. Transplantation. 2012;93(1):61-68. [28] Avkan-Oguz V, Ozkardesler S, Unek T, et al. Risk factors for early bacterial infections in liver transplantation. Transpl Proc. 2013;45(7):993-997. [29] Emery VC, Asher K, Sanjuan CJ. Importance of the cytomegalovirus seropositive recipient as a contributor to disease burden after solid organ transplantation. J Clin Virol. 2012;54(2):125-129. [30] Abate D, Saldan A, Mengoli C, et al. Comparison of CMV ELISPOT and CMV QuantiferonTM interferon-c releasing assays in assessing risk of CMV infection in kidney transplant Recipients. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51(8):2501-2507. [31] 唐志琴,王玉亮,江雁,等.肝肾移植后巨细胞病毒感染者T细胞表面CD38的动态变化[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2006, 26(3): 252-254. [32] Ticha O, Stouracova M, Kuman M, et al. Monitoring of CD38high expression in peripheral blood CD8+ lymphocytes in patients after kidney transplantation as a marker of cytomegalovirus infection. Transpl Immunol. 2010;24(1): 50-56. [33] Bestard O, Lucia M, Crespo E, et al. Pretransplant immediately early-1-specific T cell responses provide protection for CMV infection after kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2013;13:1793-1805. [34] 肖漓,石炳毅,高钰,等.HLA-G与肾移植后巨细胞病毒活动性感染的相关性研究[J].中华器官移植杂志,2011,32(9):534-538. [35] Clari MA, Munoz-Cobo B, Solano C, et al. Performance of the QuantiFERON-cytomegalovirus (CMV) assay for detection and estimation of the magnitude and functionality of the CMV-specific gamma interferon-producing CD8(+) T-cell response in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012;19(5):791-796. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||